서론
포인터를 적용해보고자 연결 리스트를 구현해보았습니다. 구현하면서 흐릿했던 포인터의 개념이 약간은 명확해졌습니다. 코드는 사람마다 다르기 때문에 흐름만 이해하고 직접 구현해보는 것을 추천합니다. (포인터, 구조체, 동적할당 개념 필요)
🔗 연결 리스트
데이터를 순서대로 저장하는 자료구조 중 하나입니다. 연결 리스트는 각각의 노드가 데이터와 다음 노드의 주소를 가지고 있는 방식으로 구현됩니다. 연결 리스트는 배열과 달리, 데이터가 메모리 상에서 연속적으로 위치하지 않기 때문에 삽입, 삭제가 용이하고 데이터 크기를 동적으로 조절할 수 있습니다.
삽입
int insertion(nval) {
struct node *newNodeptr = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newNodeptr->data = nval;
newNodeptr->nextNode = NULL;
if (headptr == NULL) {
headptr = newNodeptr;
} else {
tailptr->nextNode = newNodeptr;
}
tailptr = newNodeptr;
return 0;
};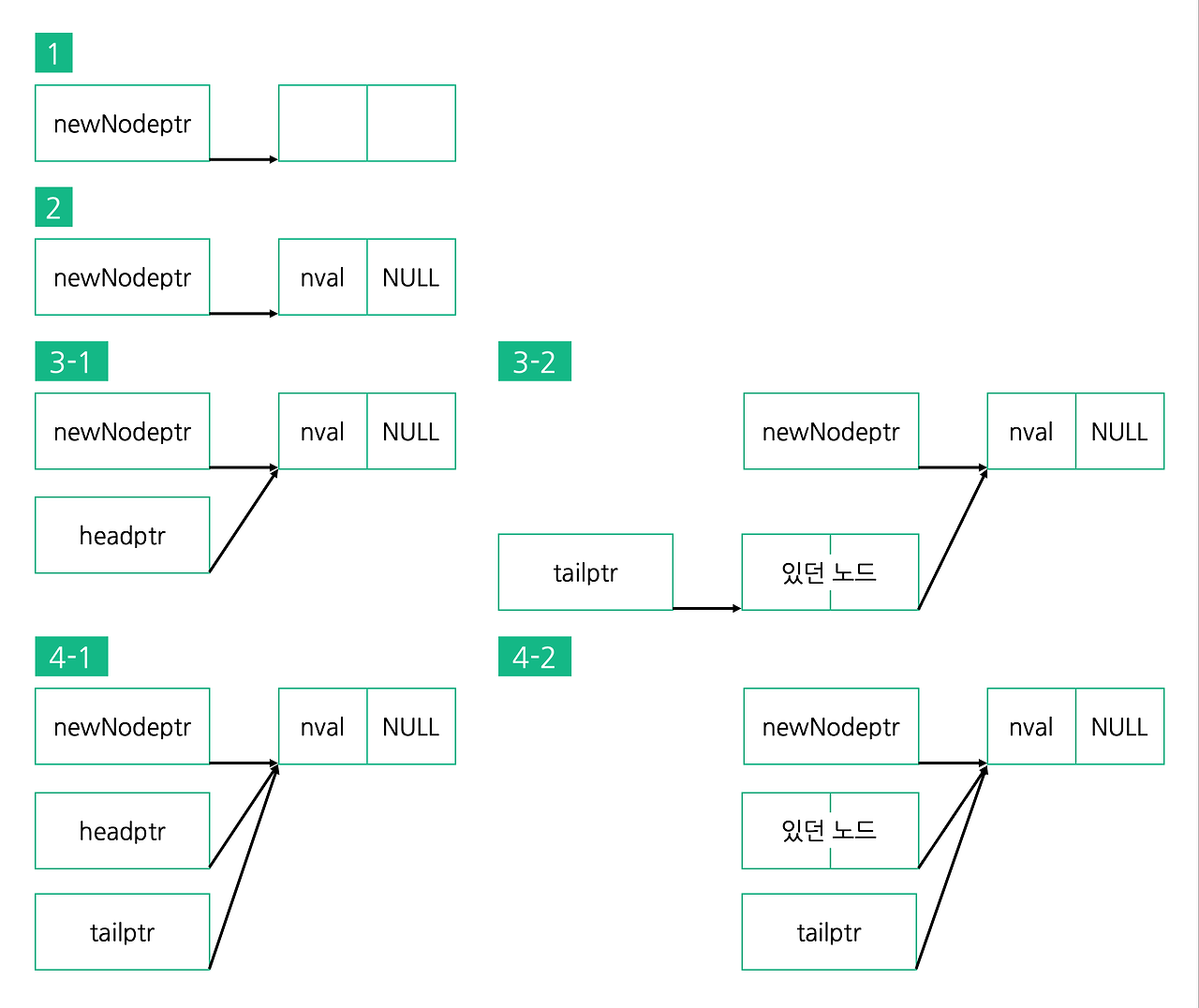
- 새로운 노드가 들어갈 수 있도록 struct node 타입 크기만큼의 메모리를 할당합니다.
- newNodeptr이 가리키는 노드의 data에 nval을 대입합니다. newNodeptr이 가리키는 노드의 nextNode에 NULL을 대입합니다.
- 현재 빈 연결리스트라면 headptr이 새 노드를 가리키도록 합니다.
아니라면 tailptr가 가리키는 노드의 nextNode가 newNodeptr가 가리키는 곳을 가리키게 합니다. - tailptr가 newNodeptr이랑 같은 곳을 가리키게 합니다.(새 노드)
삭제
int deletion(dval) {
curptr = headptr;
struct node *prevptr = NULL;
while (curptr != NULL) {
if (curptr->data == dval) {
if (prevptr == NULL) {
headptr = curptr->nextNode;
free(curptr);
return 0;
}
prevptr->nextNode = curptr->nextNode;
free(curptr);
return 0;
} else {
prevptr = curptr;
curptr = curptr->nextNode;
}
}
printf("%d를 가진 노드가 없습니다.", dval);
return 0;
};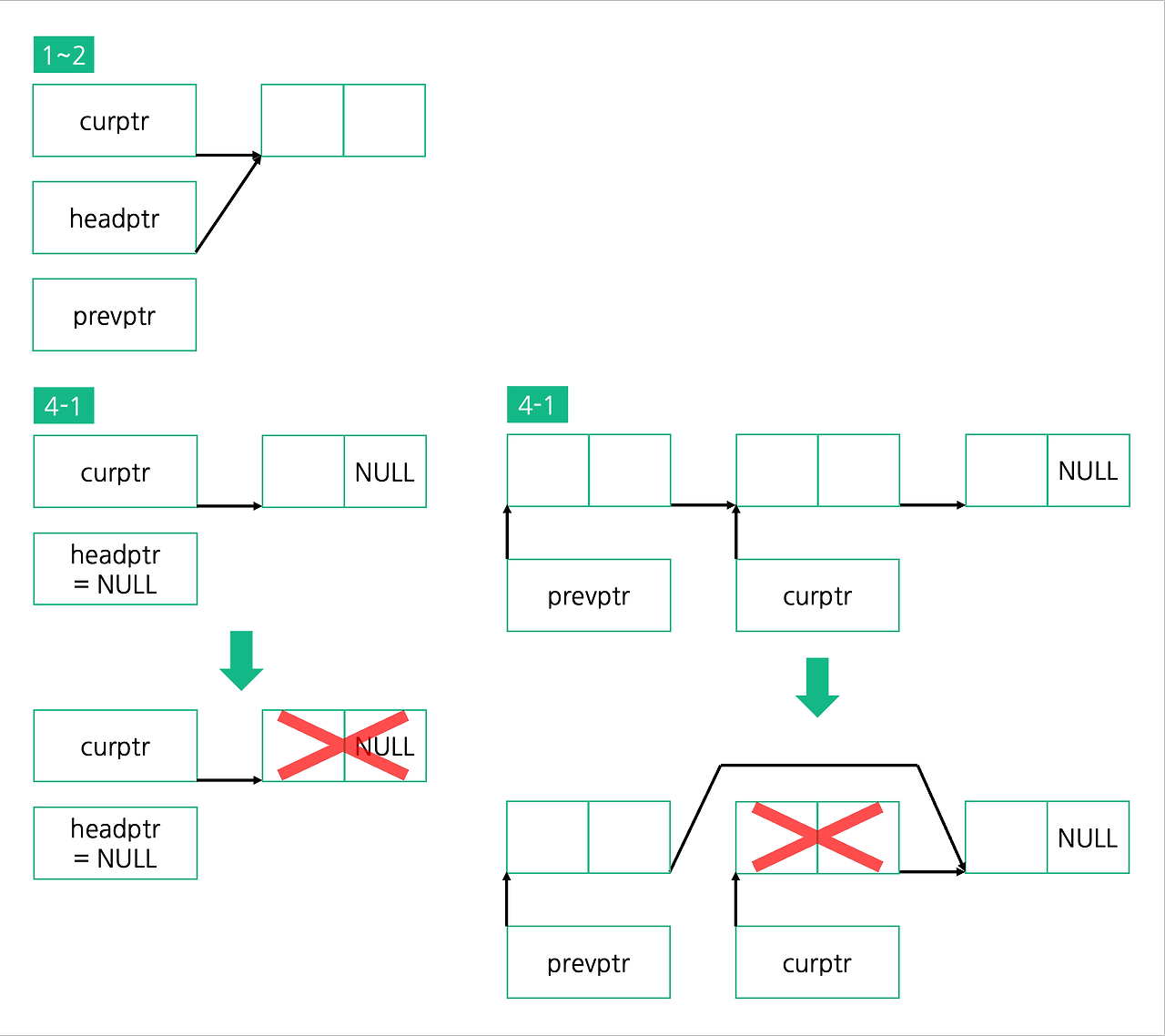
- curptr이 headptr과 같은 곳을 가리키게 합니다.
- prevptr 포인터 변수를 선언합니다.
- curptr이 NULL이 될 때까지 노드를 이동하면서 삭제하고 싶은 값을 가진 노드를 찾습니다.
- 삭제할 노드를 찾았을 때,
만약 그 노드가 첫번째 노드라면 headptr이 다음 노드를 가리키게 하고 찾은 노드에 할당된 메모리를 해제합니다.
만약 그 노드가 첫번째 노드가 아니라면 prevptr이 curptr과 같은 곳을 가리키게 하고 curptr을 해제합니다. - 아직 찾지 못했다면 다음 노드를 가리키게 하여 다시 검사합니다.
- 전체 리스트를 다 탐색해도 해당 값의 노드가 없는 경우 문구를 출력합니다.
출력
int print_list(void) {
curptr = headptr;
printf("연결 리스트: ");
while (curptr != NULL) {
printf("%d ", curptr->data);
curptr = curptr->nextNode;
}
printf("\n===============================\n");
return 0;
};headptr가 가리키는 곳부터 끝까지 curptr을 옮겨가며 출력합니다.
📄 전체 코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 노드 구조체 만들기
struct node {
int data;
struct node *nextNode;
};
// 포인터 만들기
struct node *headptr = NULL;
struct node *tailptr = NULL;
struct node *curptr = NULL;
// 새 노드를 삽입하는 함수
int insertion(nval) {
struct node *newNodeptr = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newNodeptr->data = nval;
newNodeptr->nextNode = NULL;
if (headptr == NULL) {
headptr = newNodeptr;
} else {
tailptr->nextNode = newNodeptr;
}
tailptr = newNodeptr;
return 0;
};
// 입력받은 값의 노드를 삭제하는 함수
int deletion(dval) {
curptr = headptr;
struct node *prevptr = NULL;
while (curptr != NULL) {
if (curptr->data == dval) {
if (prevptr == NULL) {
headptr = curptr->nextNode;
free(curptr);
return 0;
}
prevptr->nextNode = curptr->nextNode;
free(curptr);
return 0;
} else {
prevptr = curptr;
curptr = curptr->nextNode;
}
}
printf("%d를 가진 노드가 없습니다.", dval);
return 0;
};
// 연결 리스트를 출력하는 함수
int print_list(void) {
curptr = headptr;
printf("연결 리스트: ");
while (curptr != NULL) {
printf("%d ", curptr->data);
curptr = curptr->nextNode;
}
printf("\n===============================\n");
return 0;
};
// 입력값을 받는 함수
int ask() {
int answer;
int newval; // 새로 받아오는 입력값(노드의 data 값)
int delval; // 삭제하고 싶은 값
// 만약 포인터가 어떠한 노드도 가리키고 있지 않다면
if (headptr == NULL && tailptr == NULL) {
printf("리스트가 비어있습니다.\n");
}
printf("하고 싶은 동작을 입력하세요.\n");
printf("1. 삽입 2. 삭제\n");
scanf("%d", &answer);
if (answer == 1) {
printf("추가하고 싶은 값을 입력하세요.\n");
scanf("%d", &newval);
insertion(newval);
} else if (answer == 2) {
printf("삭제하고 싶은 값을 입력하세요.\n");
scanf("%d", &delval);
deletion(delval);
} else if (headptr != NULL && tailptr != NULL) {
printf("첫 값: %d, 마지막 값: %d \n", headptr->data, tailptr->data);
};
print_list();
return 0;
};
int main(void) {
while (1) {
ask();
}
}참고자료
- <씹어먹는 C언어> - 이재범
- <윤성우의 열혈 자료구조> - 윤성우
'자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 레드 블랙트리(The red black tree): 규칙, 회전, 삽입 (0) | 2024.07.15 |
|---|

